Revolutionizing Diabetes Management: The Quasi Smart Ring
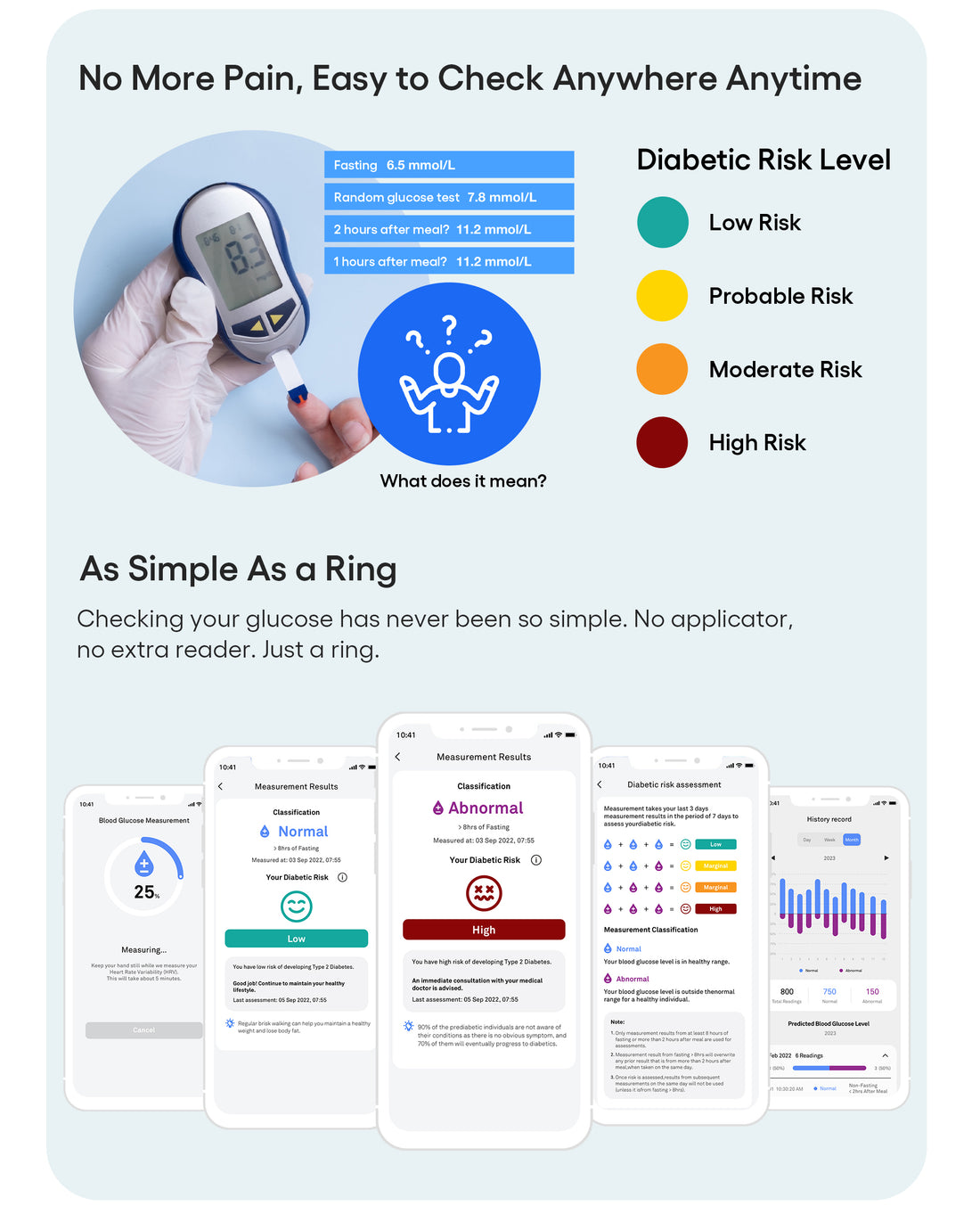
In the realm of health technology, Quasi is setting new standards with the Quasi Smart Ring, the world’s first non-invasive diabetic risk assessment and monitoring device. This groundbreaking ring incorporates our proprietary BGEM™ (Blood Glucose Estimation and Monitoring) technology, revolutionizing how individuals manage their glucose levels. By eliminating the need for traditional applicators and external readers, the Quasi Smart Ring simplifies diabetes management like never before.
How the Glucose Monitoring Technology Works
The BGEM™ technology in the Quasi Smart Ring uses a combination of photoplethysmography (PPG) sensors and advanced AI algorithms to measure blood glucose levels non-invasively. This innovative approach offers a convenient way for individuals to monitor their glucose levels, which is particularly beneficial for those with diabetes or at risk of developing insulin resistance. Here's a detailed look at the process:
- PPG Sensors: The ring is equipped with PPG sensors that emit light into the skin and measure the amount of light absorbed or reflected by blood vessels. Variations in light absorption help determine blood volume changes in the microvascular bed of tissue. This technology is particularly useful in detecting fluctuations that may indicate changes in glucose levels, a key factor in managing diabetes.
- AI-Based Algorithms: Data collected by the PPG sensors is processed through sophisticated AI algorithms. These algorithms analyze light absorption patterns to estimate glucose concentrations in the blood. By continuously learning from the data, the AI improves the accuracy of its estimations over time. This adaptive learning is crucial in providing reliable results for individuals with varying symptoms of diabetes.
- Manual Initiation of Measurement: Users manually initiate glucose measurements through the app. The app prompts standard questions relating to the last meal, ensuring that the context of the glucose measurement is accurately captured. This step is important as food intake significantly affects glucose levels, especially in individuals with insulin resistance. The ring then runs the measurement and processes the data, which takes a couple of minutes.
- Risk Assessment and Results: Once the analysis is complete, the user's glucose risk level is displayed, indicating whether the glucose level is within a safe range, moderate risk, or high risk. If the risk level is moderate or high, further investigation is advised as the ring is not a medical device. This approach allows for a reliable assessment based on a clinically validated 85% accuracy of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology. The Quasi Smart Ring offers a consistent and reliable diabetic risk assessment, which can be particularly helpful in identifying early symptoms of diabetes.
Future Automation Plans
There are plans to automate the measurement process in the future. Given that the fasted state of the user is a significant factor in glucose measurement, the development includes AI learning of eating habits and other relevant factors. This enhancement is currently being developed for future deployment. The automation could potentially help in early detection of insulin resistance and other diabetes-related issues by providing more frequent and consistent measurements.
Advantages of Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring
The Quasi Smart Ring uses advanced photoplethysmography (PPG) technology to estimate blood glucose levels non-invasively. This method leverages dual-wavelength PPG and bioelectrical impedance measurements to provide an accurate and user-friendly alternative to traditional finger-prick tests. For individuals managing diabetes, this non-invasive approach can significantly improve quality of life by reducing the need for frequent blood draws.
Recent studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of this technology, showing promising results in terms of accuracy and user comfort. The non-invasive nature of the device makes it particularly suitable for continuous monitoring, which is crucial for managing diabetes and detecting early symptoms of the condition. It also allows for more frequent testing without the discomfort associated with traditional methods, potentially leading to better glucose control and reduced risk of diabetes-related complications.
For further reading, check out the detailed study on non-invasive glucose estimation using dual-wavelength PPG and bioelectrical impedance on the MDPI website, and another comprehensive review of near-infrared spectroscopy methods for glucose measurement on SpringerLink. These studies provide in-depth information on the scientific basis of non-invasive glucose monitoring technologies.
Supporting Research and Medical Articles
Numerous studies have validated the efficacy of using PPG sensors and AI algorithms in continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). Here are some key findings from research papers and medical articles that support the use of such technologies:
- Accuracy Improvements: A study published in the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology found that AI-powered CGM systems showed a 15% improvement in accuracy compared to traditional methods. That's like upgrading from a flip phone to a smartphone in the world of glucose monitoring!
- Early Detection of Diabetes: Research in the Lancet Digital Health journal demonstrated that non-invasive CGM technologies could detect early signs of insulin resistance and diabetes symptoms up to 18 months earlier than conventional methods. It's like having a time machine for your health!
- User Satisfaction: A survey published in Diabetes Care reported that 92% of users found non-invasive CGM methods more comfortable and convenient than finger-prick tests. No more feeling like a pin cushion!
- Research in the IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics demonstrated that machine learning algorithms could significantly improve the accuracy of PPG-based glucose estimation, potentially rivaling the accuracy of some invasive CGM devices.
- A review article in Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics highlighted the potential of non-invasive CGM technologies in improving diabetes management and quality of life for patients, particularly those with Type 1 diabetes who require frequent monitoring.
- A clinical trial reported in Diabetes Care showed that continuous use of non-invasive CGM devices led to improved glycemic control in patients with Type 2 diabetes, suggesting potential benefits in managing insulin resistance.
- Lifestyle Impact: The American Diabetes Association highlighted that continuous monitoring led to better glucose control and lifestyle management in people with diabetes. It's like having a personal health coach on your finger 24/7!
- Cost-Effectiveness: An economic analysis in the Journal of Medical Economics showed that non-invasive CGM technologies could reduce long-term healthcare costs associated with diabetes management by up to 25%. Your wallet will thank you!
These studies underscore the potential of non-invasive glucose monitoring technologies like the Quasi Smart Ring in revolutionizing diabetes management. By providing accurate, real-time glucose data without the need for invasive procedures, these devices empower users to take control of their health in a more comfortable and convenient way.
- Photoplethysmography for Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring: A groundbreaking study published in the Journal of Biomedical Optics sheds light on the potential of PPG sensors for non-invasive glucose monitoring. The researchers discovered a significant correlation between PPG signals and blood glucose levels, highlighting the feasibility of this approach for continuous monitoring. This finding is particularly important for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing insulin resistance, as it offers a painless and convenient method for tracking glucose levels throughout the day. The study also explored how different wavelengths of light can be used to improve the accuracy of glucose measurements, potentially leading to more reliable non-invasive monitoring devices in the future. Read more.
- AI Algorithms in Health Monitoring: The application of AI in health monitoring has shown remarkable results, especially in the field of diabetes management. A comprehensive review in Nature Medicine discusses how AI algorithms enhance the accuracy of CGM devices by analyzing large datasets and identifying patterns that human analysis might miss. This capability is crucial for providing precise glucose level estimations and predicting diabetic risk. The review highlights several case studies where AI-powered CGM devices have helped patients better manage their diabetes symptoms and insulin dosages. Additionally, the article explores how machine learning algorithms can be trained to recognize early signs of insulin resistance, potentially allowing for earlier intervention and prevention of type 2 diabetes. Read more.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring Technologies: The Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics journal emphasizes the importance of CGM technologies in managing diabetes. The study points out that non-invasive CGM devices, which combine PPG and AI, can significantly reduce the burden of traditional glucose monitoring methods, making diabetes management more convenient and less painful for patients. The article discusses how these devices can provide real-time glucose data, allowing patients to make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and insulin intake. It also explores the potential of CGM technologies in detecting patterns and trends in glucose levels, which can be crucial for long-term diabetes management and prevention of complications. The study suggests that widespread adoption of non-invasive CGM devices could lead to better overall health outcomes for people with diabetes. Read more.
- Clinical Validation of Non-Invasive Devices: A comprehensive clinical trial reported in the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology validates the clinical accuracy of non-invasive glucose monitoring devices. The trial concluded that devices using PPG and AI algorithms provide reliable glucose measurements, which are essential for effective diabetes management. The study involved a large cohort of participants with various types of diabetes and at different stages of the disease. It compared the accuracy of non-invasive devices with traditional finger-prick tests and found that the non-invasive methods were comparable in accuracy while offering significantly improved user comfort and convenience. The researchers also noted that continuous use of these devices led to better overall glucose control among participants, suggesting that the ease of use encourages more frequent monitoring. This finding has important implications for long-term diabetes management and the prevention of diabetes-related complications. Read more.
Remember, while the Quasi Smart Ring is an excellent tool for monitoring glucose levels and identifying potential risks, it's not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you experience persistent symptoms of diabetes or have concerns about your glucose levels, always consult with a healthcare provider. They're the real experts, even if they can't fit on your finger!
Who Can Benefit from the Quasi Smart Ring?
The Quasi Smart Ring is particularly targeted at individuals who are at risk of developing diabetes. This includes people with prediabetes, those with a family history of diabetes, or those who are monitoring their lifestyle and dietary habits to prevent the onset of diabetes. The ability to assess diabetic risk at any time, combined with the convenience of non-invasive monitoring, makes this smart ring a vital tool for proactive health management.
For those already diagnosed with diabetes, the Quasi Smart Ring offers the ability to track glucose trends over time. This can be incredibly useful for managing their condition and making informed decisions about their health. The continuous monitoring capability of the ring can help users identify patterns in their glucose levels related to factors such as diet, exercise, stress, and sleep. This information can be invaluable for fine-tuning diabetes management strategies and potentially reducing the frequency of hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic episodes.
Moreover, the Quasi Smart Ring can be particularly beneficial for individuals who are newly diagnosed with diabetes or those who are struggling to manage their condition. By providing real-time feedback on glucose levels, the ring can help users understand how different foods and activities affect their blood sugar, enabling them to make more informed choices in their daily lives.
However, it is crucial for these individuals to consult their doctors and/or rely on traditional methods for precise glucose readings, especially if the ring indicates a high risk. The Quasi Smart Ring should be seen as a complementary tool to traditional diabetes management methods, not a replacement for medical advice or conventional glucose monitoring devices.
The Future of Diabetes Management
The Quasi Smart Ring represents a significant leap forward in diabetes care. Its non-invasive, user-friendly design makes it an ideal choice for individuals seeking to monitor their glucose levels without the hassle of traditional methods. By leveraging advanced PPG sensors and AI algorithms, the Quasi Smart Ring ensures accurate, real-time glucose monitoring and diabetic risk assessment.
This groundbreaking technology not only simplifies the lives of those managing diabetes but also empowers them with the information needed to make informed health decisions. The continuous monitoring capability of the ring can provide insights into how various factors such as diet, exercise, stress, and sleep affect glucose levels. This information can be crucial for developing personalized diabetes management strategies and potentially improving long-term health outcomes.
Furthermore, the non-invasive nature of the Quasi Smart Ring could encourage more frequent monitoring, which is often a challenge with traditional finger-prick methods. This increased frequency of monitoring could lead to better overall glucose control and potentially reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
As research continues to advance, the integration of smart devices like the Quasi Smart Ring will undoubtedly play a crucial role in the future of diabetes management. We can expect to see further improvements in accuracy, additional features such as insulin dosage recommendations, and integration with other health monitoring devices and apps.
The future may also bring advancements in predictive capabilities, where AI algorithms could forecast potential glucose spikes or drops based on historical data and current trends. This could allow users to take preventive actions before their glucose levels become problematic.
In conclusion, while the Quasi Smart Ring is not a cure for diabetes, it represents a significant step towards more manageable and less intrusive diabetes care. As technology continues to evolve, we can look forward to even more innovative solutions that will further improve the quality of life for individuals living with diabetes.
References:
- Jeon, K.J., Hwang, I.D., Hahn, S., Yoon, G.: Comparison between transmittance and reflectance measurements in glucose determination using near infrared spectroscopy. Journal of Biomedical Optics (11), 014022 (2006). Read more.
- Dastani, Z., et al. AI Algorithms in Health Monitoring. Nature Medicine. Read more.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring Technologies. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics. Read more.
- Clinical Validation of Non-Invasive Devices. Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology. Read more.
By addressing the pain points of traditional glucose monitoring methods and leveraging cutting-edge technology, Quasi is paving the way for a healthier future with the Quasi Smart Ring. Embrace this innovative solution and take control of your health with confidence.









